10.5% CAGR from 2018-2024
2017 2024
$1.024 billion $2.043 billion
Market growth from
Heart failure increases
Lack of suitable organ donors
Growing device/therapy approvals
Technological product design advancements
Comparison
Pulsatile-flow
Internal chamber, inflow/outflow valves, pneumatic or electric driven
Large diameter percutaneous leads
Loud functioning sound
High friction in pump
High morbidity (hemolysis)
Continuous-flow
Non-pulsatile flow: no valves, small cannulas, magnetically coupled motor (direct-drive, self-bearing, or bearing-less), or axial rotor
Quieter, better durability (simpler mechanics)
Increased blood flow (10L/min) reduced blood stasis and hemolysis
Component functions
Inflow cannula: Drains blood from left ventricle/left atrium
Mechanical impella (pump): Propels blood
Outflow cannula: Returns blood to aorta
Drive line: Connects to external portable driver, power supply
Uses
Destination therapy
Bridge-to-transplantation
Bridge-to-recovery
Globally
Largest share of market – Bridge-to-transplant
Fastest growing segment – Destination therapy
Major market share – North America
Fastest growth rate – Asia-Pacificp
Key players
Abbot Laboratories
Abiomed
Berlin Heart
Thoratec
Jarvik Heart
Heart Ware
Apaxis
CorWave
Evaheart
Reliantheart
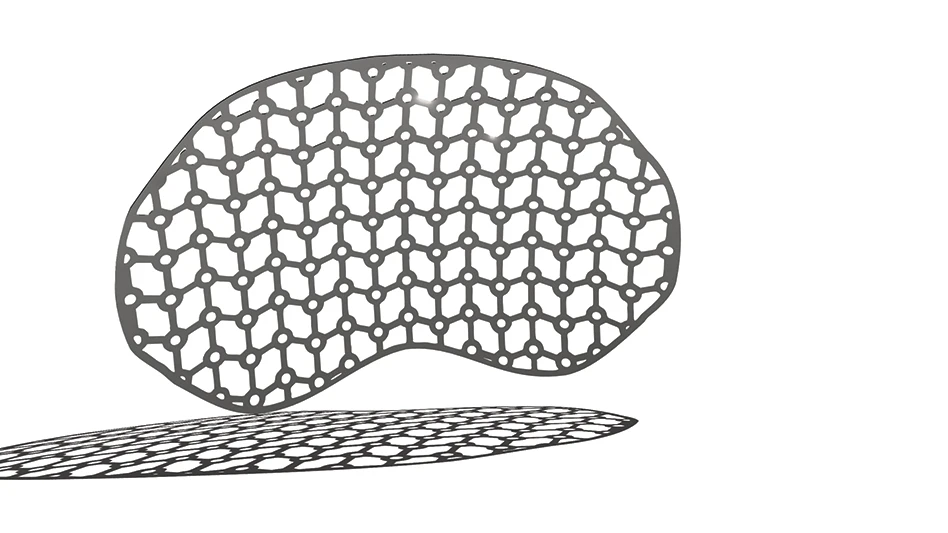
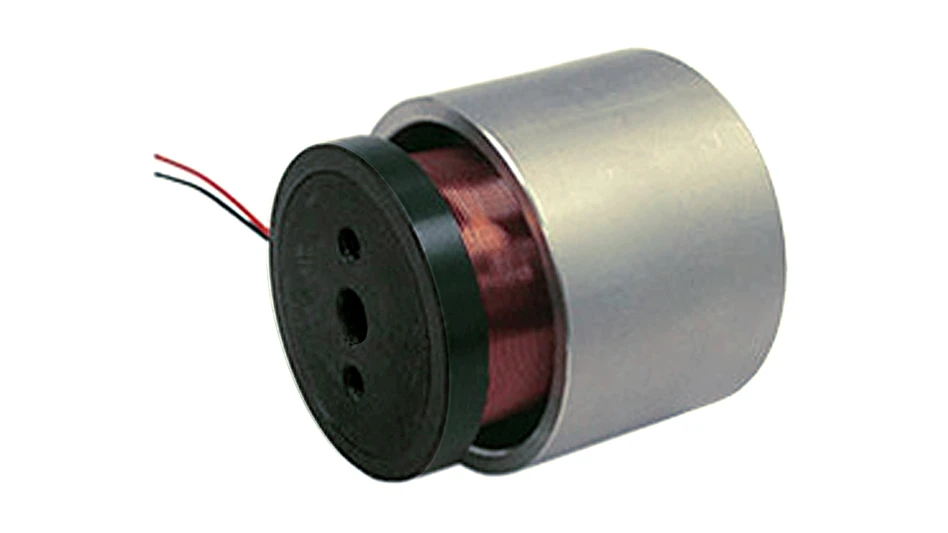
MAIN Image: courtesy of St. Jude Medical Inc / INSET: Courtesy of ReliantHeart.com

Explore the May 2018 Issue
Check out more from this issue and find your next story to read.
Latest from Today's Medical Developments
- Stryker’s flexible syndesmotic fixation device stabilizes ankle injuries
- Mergers & acquisitions news: MGS, Quantum Surgical bolster medtech portfolios
- Exchangeable-head solid carbide cutting tools
- NextDent 300 MultiJet printer delivers a “Coming of Age for Digital Dentistry” at Evolution Dental Solutions
- Get recognized for bringing manufacturing back to North America
- Adaptive Coolant Flow improves energy efficiency
- VOLTAS opens coworking space for medical device manufacturers
- MEMS accelerometer for medical implants, wearables