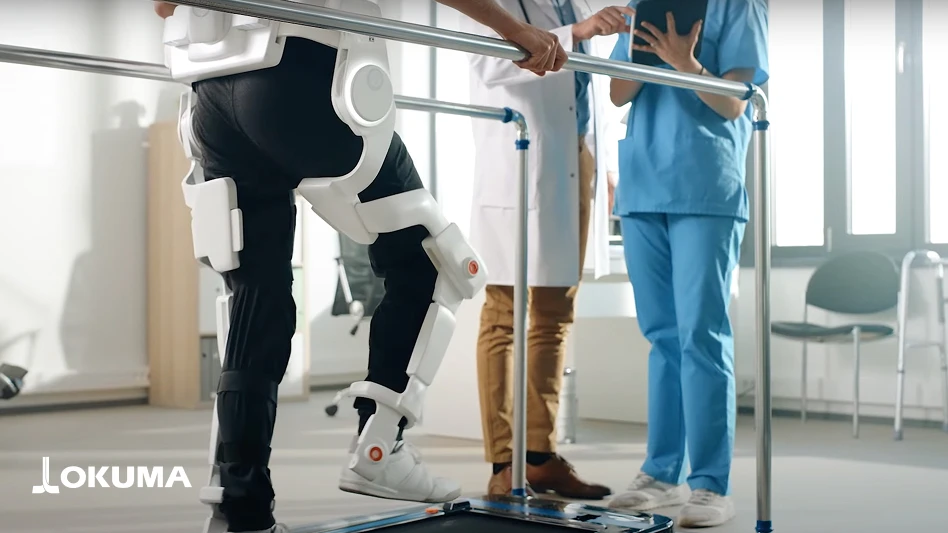
Implantable for Severe Paralysis: The technology uses implanted electrodes to collect movement signals from the brain and decode them into movement commands. Shown to restore voluntary motor impulses in patients with severe paralysis.
Approximately one in 50 Americans, or 5.4 million people, have some form of paralysis. Most patients experience a significant decline in their overall health. Recently, a team has offered new hope for these patients by leveraging implanted brain-computer interface technology to recover lost motor control and enable patients to control digital devices. The technology uses implanted electrodes to collect movement signals from the brain and decode them into movement commands. It has been shown to restore voluntary motor impulses in patients with severe paralysis due to brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerve or muscle dysfunction. While the interface technology is in its infancy, the FDA has designated the implantable a “breakthrough device,” reinforcing the need to move this technology to the bedside of patients who need it most.
Latest from Today's Medical Developments
- The need for speed in high-speed machining
- FUCHS Lubricants’ NYEMED 7312
- Localizing robotics: Yaskawa's commitment to American manufacturing
- OPEN MIND Technologies’ hyperMILL 2025 CAM software innovations, enhancements
- July Lunch + Learn with SW North America
- Stryker raises full-year guidance despite muted investor reaction
- Unlocking 3D vision: Basler AG launches Stereo ace camera series
- Lisa Anderson, supply chain & manufacturing expert, comments on the One Big Beautiful Act and its implications for US manufacturers