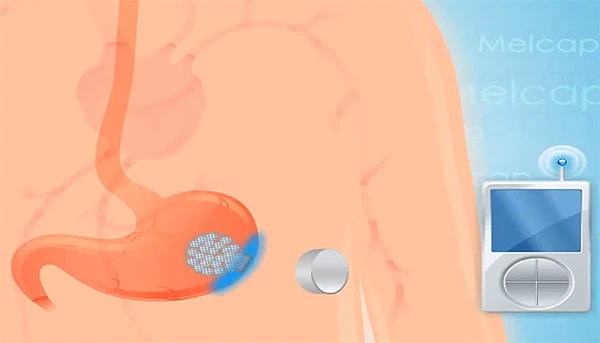
Israeli-based MelCap offers an innovative system based on a guided disposable ingestible autonomous wireless stimulating capsule with variable volume positioned in the human Gastrointestinal Tract (GI) and fixed at a targeted location by a magnetic system attached to the body [non-invasively].The capsule is wirelessly controlled from outside. Company officials have applied for the IP protection, and recently got patent allowance from the U.S. Patent Office, which claimed various designs of the capsule and the system.
MelCap capsule is the size of a large pill and is swallowed so that once in the stomach, an external magnet is used to correctly position the capsule.
2.1 billion people – about 30% of the global population – are overweight or obese and that about 15% of health-care costs in developed economies are driven by it.
The innovation is based on a guided, disposable, swallowable capsule positioned in the human gastrointestinal tract (GI) and fixed by a magnetic system attached to the body [non-invasive]. The capsule is wirelessly controlled from outside.
How it works:
The MelCap system has three main parts
- Remotely controlled capsule adapted for ingestion or placement into the gastrointestinal tract (GT) of a patient
- Remote control device for controlling and sharing information with the capsule
- Magnetic coupling system for fixing the capsule within the gastrointestinal tract of the patient
Beginning steps
- Following swallowing of the capsule by the patient, the capsule enters the GT.
- Location of the capsule within the GT is defined by an external magnetic field sensor.
- Further, the position of the capsule relative to the targeted nerve is determined by method of Nerve Conduction Study (NCS).
- At the required location the capsule is secured to an inner wall of the GT by the magnetic attraction between the magnetic element in the capsule and the magnetic element in the external positioning unit
Last steps
- The patient and/or medical personnel activate the capsule wirelessly by transmitting operating instructions to the capsule from the remote wireless control unit.
- The capsule receives the operating instructions and configures and activates a pulse generator, contained in the capsule, to generate electrical pulses which propagate through the GT in proximity to at least one chosen area of GI tract
- The pulses activate for instance a vagus nerve, thus enhancing the gastro motility
- Depending on location of the capsule in the GT it can have different clinical effects: Gastric electrical stimulation (GES), Lower Esophagus Sphincter (LES) muscle simulation or vagus nerve blocking which require continuous monitoring and treatment
Source: Melcap
Latest from Today's Medical Developments
- NextDent 300 MultiJet printer delivers a “Coming of Age for Digital Dentistry” at Evolution Dental Solutions
- Get recognized for bringing manufacturing back to North America
- Adaptive Coolant Flow improves energy efficiency
- VOLTAS opens coworking space for medical device manufacturers
- MEMS accelerometer for medical implants, wearables
- The compact, complex capabilities of photochemical etching
- Moticont introduces compact, linear voice coil motor
- Manufacturing technology orders reach record high in December 2025





